
SOLUTIONS
Automated Content Publishing Solution
Fully automated end-2-end VOD publishing starting with complete content packages to be processed and published
Why is VOD Publishing more than just transcoding and uploading?
To give an answer we need to question what the origin of the content to publish is and whether it is ready to be published. Based on the answer we do distinguish in fully automated content publishing and partly manual content aggregation + fully automated publishing. This article describes the fully automated end-2-end process, starting with complete content packages to be processed and published. The following article describes the end-2-end process starting with the content aggregation: VOD Content Aggregation and Publishing end-2-end Solution.
The VOD publishing business process - more than just a transcode and file transfer
Larger Video On Demand portals are based on the content from multiple sources that either supply content continuously or in bursts. Usually, the required asset set (e.g. video, audio in multiple languages, subtitles in multiple languages, trailer, posters, thumbnails, scrubber boards, descriptive, and technical metadata) is well defined. Content suppliers are asked to deliver in a normalized form. So far the theory.
Technical, operational, business, or legal reasons might cause asset packages to be formed differently or incomplete. As long as a certain contributor always sends files in a differing form, the ingest workflow can handle that and reform to the expected normalized form. And to a certain degree, missing essences can be automatically generated or retrieved from existing sources or partner companies.
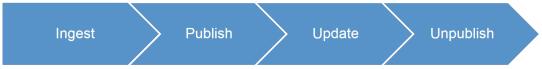
Once asset packages are received in an expected form, audiovisual essences can be transcoded, checked, and, on success, uploaded to the CDN. Pictures can be re-rendered, scrubber boards can be retrieved and stitched, and metadata can be reformed. Finally, all such essences and metadata are uploaded to the CMS for automatic or manual publishing.
It might happen that the audiovisual content changes, or pictures and metadata are updated. On these occasions, a reprocessing and update publishing takes place.
And finally, once the publishing end date is reached, all expired assets are automatically deleted from the CDN and the CMS catalogue.
network architecture
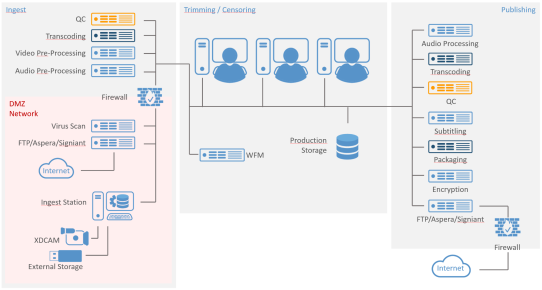
What does the service architecture of our VOD Publishing Solution look like?
The Workflow Manager (short: WFM) is the central workflow orchestration and fully automatic processing engine. It connects to all processing services. Such services can be located on-premise, in the cloud, or contributed by third-party services. As it controls the end-2-end processing also allows to monitor the progress of every asset to be published.
All other processing services like file transfer, virus checking, audio processing (e.g. loudness), video processing (e.g. standard conversions), transcoding, subtitling, metadata transformation, CDN and CMS are managed from the Workflow Manager via API calls.
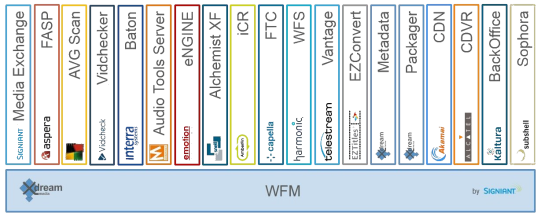
Who are the product partners for our VOD Publishing Solution?



Workflow Management
File Transcoding
publishing CMS

B2B accelerated file transfer

Quality Control




